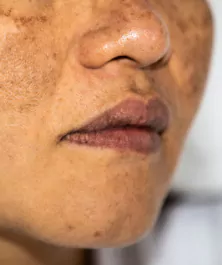
Hyperpigmentation of the skin is when a portion of the skin is darker than the other surrounding areas. This occurs due to melanin. Melanin is the pigment that is produced by cells called melanocytes. Melanin gives the skin its color. When the skin produces more melanin, it leads to hyperpigmentation.
Why are lips differently colored than regular skin?
Our skin is made up of many layers of cells whereas our lips are composed of only three to five layers of cells. This means that we have thinner skin on the lips. The pinkish or crimson color of the lips comes from the many networks of blood capillaries present just beneath the thin skin over the lips.
Why are some lips darker than the others?
1. Ethnicity: The lips come in a variety of colors and shades. Some people have lips with a more pinkish tone, whereas others have them more in a purplish – or even olive – tone. It all boils down to genetics and race. Those who are fair-complexioned tend to have rosy lips whereas those with darker skin have purplish lips. However, this is not a sure shot rule.
2. Smoking: Cigarettes contain various toxins that can harm your health, leading to conditions ranging from emphysema to cancers. smoking can also affect the lip color. People who smoke regularly have hyperpigmented lips. Nicotine is the main culprit.
3. Pan chewing: The betel nut is chewed with betel leaf and lime as a recreational candy. It also acts as a stimulant and even as a digestive aid. Pan contains betel leaf and betel nut. Chewing pan for a long time can cause hyperpigmentation of the lips.
4. Coffee, tea and other staining liquids: As is evident from their ability to stain cups and mugs, these liquid beverages can also stain lips and teeth. Reducing consumption of these liquids, can reduce hyperpigmentation of the lip.
5. Prolonged sun exposure: Increased UV exposure can cause the melanocytes to overproduce melanin (skin pigment). This leads to hyperpigmentation of the lips.
6. Hemochromatosis: An abundance of iron in the body can also lead to lip hyperpigmentation.
7. Melanin-making medication:
- People who take too many painkillers, especially NSAIDS (non-steroidal anti inflammatory drugs) due to either an acute condition like multiple fractures after an accident or a chronic condition like arthritis can expect lip hyperpigmentation.
- Antimicrobial drugs like sulfonamides, cyclophosphamide, doxorubicin are taken by cancer patients during cancer therapy. These drugs also cause lip hyperpigmentation.
- If you have anxiety, you must have heard the names of medications like escitalopram and barbiturates. These drugs help to relax the nervous system, but also darken the lips.
- Levodopa causes lip hyperpigmentation. It is a drug taken by those who have Parkinson’s disease.
- Antifungal drugs like ketoconazole can also cause the lips to be hyperpigmented.
- Colchicine is taken by gout patients. Be aware as it also causes lips to darken.
8. Various clinical diseases: Some people can also have lip hyperpigmentation due to some diseases, like:
- Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation
- Lichen planus
- Lupus erythematosus
- Lentigines
- Nevus
- Peutz-Jeghers syndrome
- Bandler syndrome
- LEOPARD syndrome
- Endocrine and metabolic disorders
- Addison’s disease
- Cushing’s disease
- Nelson’s syndrome
- Acromegaly
- Hyperthyroidism
- Heavy metal poisoning
9. Cancer: Various benign and malignant cancers can cause lip hyperpigmentation. These include:
- Kaposi’s sarcoma
- Malignant melanoma
- Cavernous hemangioma
- Benign pigmented lesions
- Malignant pigmented lesions
How can I prevent lip hyperpigmentation?
- Quit smoking
- Limit your sun exposure
- Always wear sunscreen. There are various lip balms and lip products that come with SPF.
- Hats are good to make a fashion statement as well as keep your face and lips protected from harsh UV rays if they are wide-brimmed.
How do I treat lip hyperpigmentation?
- Lip hyperpigmentation can be treated by first treating the underlying cause.
- For instance, if it is deduced that this lip discoloration is due to a certain medication, then that medication can be changed by your doctor.
- Laser therapy
- Cryotherapy
- Surgery
- Intense Pulse Light (IPL)
- Photodynamic therapy
- Topical bleaching agents
Resource:
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17241433/
Haresaku S, Hanioka T, Tsutsui A, Watanabe T. Association of lip pigmentation with smoking and gingival melanin pigmentation. Oral Dis. 2007 Jan;13(1):71-6. doi: 10.1111/j.1601-0825.2006.01249.x. PMID: 17241433.